Improving the Efficacy of Ultra-Low-Field MRI Using AI
Overview
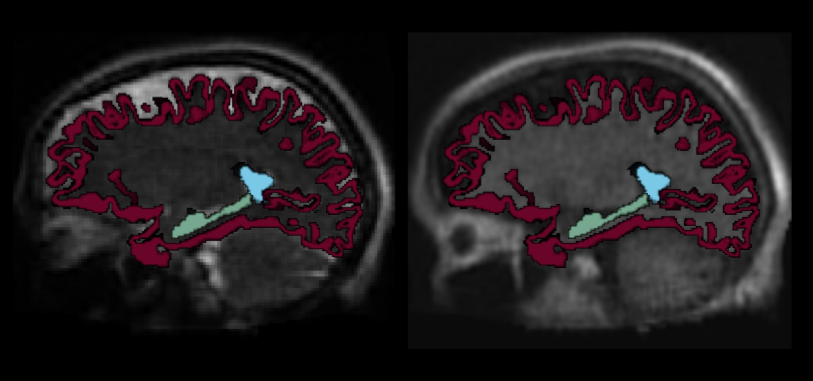
In this project we aim to develop AI methods to improve the image quality of ultra-low-field MRI.
The accessibility of MRI is limited by logistical and economic constraints. Approximately 70 percent of the world’s population currently has little or no access to this imaging modality. Where access exists, MRI may be unavailable or of limited use to patients who have contraindications such as metal implants or claustrophobia. The same limitations also constrain research investigations that rely on MRI scans.
Now, new developments in ultra-low-field (ULF) MRI technology hold the promise to improve the mobility and accessibility of MRI. This promise extents to facilitating longitudinal and population-representative normative aging studies that can help researchers develop more accurate aging biomarkers and a deeper understanding of aging-related health disparities. Relative to conventional MRI, ULF MRI is currently challenged by low signal-to-noise ratio, long scan times, and low special resolution—challenges that must be overcome for ULF MRI to realize its potential.
In this collaborative project, we aim to address some of the key limitations of ULF MRI by developing AI methods that improve the image quality. Better images from ultra-low-field systems stand to make such systems more efficient in both clinical radiology and neuroscientific research.
Keywords
- Low-field MRI
- Image Analysis
- Deep Learning
Project Team

Jelle Veraart, PhD
Project Lead
External Collaborators
- Jong Chul Ye, Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology (KAIST)
Publications
- Hsu P, Marchetto E, Sodickson DK, Johnson PM, Veraart J. Morphological Brain Analysis Using Ultra Low-Field MRI. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025;46(10):e70232. doi:10.1002/hbm.70232
Acknowledgements
This research is part of a collaboration with NYU-KAIST Global Health Initiative and the Korean AI Flagship Project—National AI Research Lab and is performed under the rubric of the Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research (CAI2R), a NIBIB Biomedical Technology Resource Center (NIH P41EB017183).






